Fireplaces are a popular feature in many homes during the winter months. They provide warmth, comfort, and a visually appealing focal point. However, the actual heat they deliver varies significantly depending on the type of fireplace and its efficiency. Below, we summarize the typical heat output of wood, gas, and electric fireplaces.
Understanding Heat Output
BTU per hour is the standard measure of heat output for fireplaces. While a fireplace’s BTU rating indicates potential energy production, the amount of heat that actually reaches the living space depends on the appliance’s design, fuel type, and room conditions. Additionally, some heat can be lost through chimneys, vents, or flues, reducing the overall warmth felt in the room.
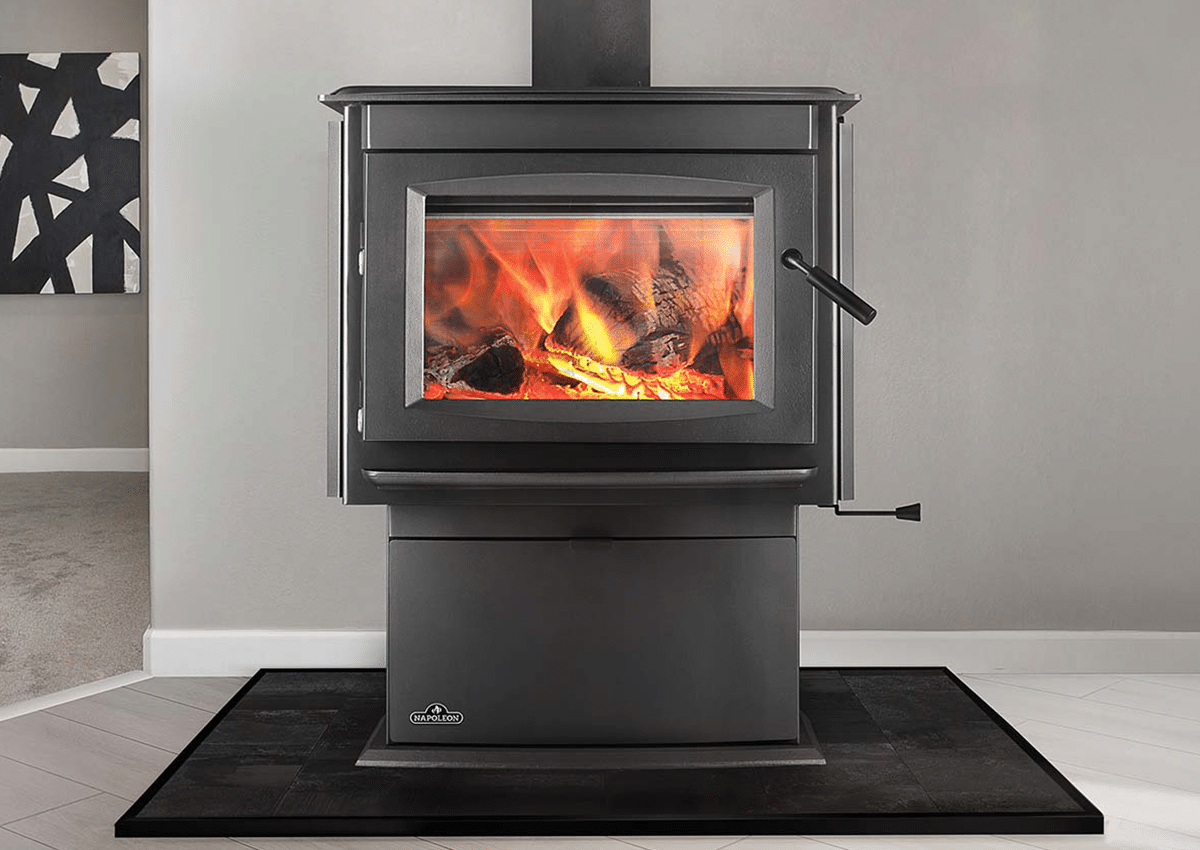
Wood Fireplaces
Traditional wood-burning fireplaces provide the classic fire experience with visible flames, crackling logs, and the scent of burning wood. However, their heat output is often lower than people expect.
Open hearth wood fireplaces can generate 20,000 to 40,000 BTU per hour, but much of this heat escapes through the chimney. Modern wood fireplaces can produce 40,000 to 80,000 BTU per hour, transferring more heat into the room and improving overall efficiency.
Wood fireplaces are best for creating a cozy atmosphere and warming the immediate area near the hearth. Actual heat delivered to the room will vary depending on wood type, moisture content, fire size, and airflow.
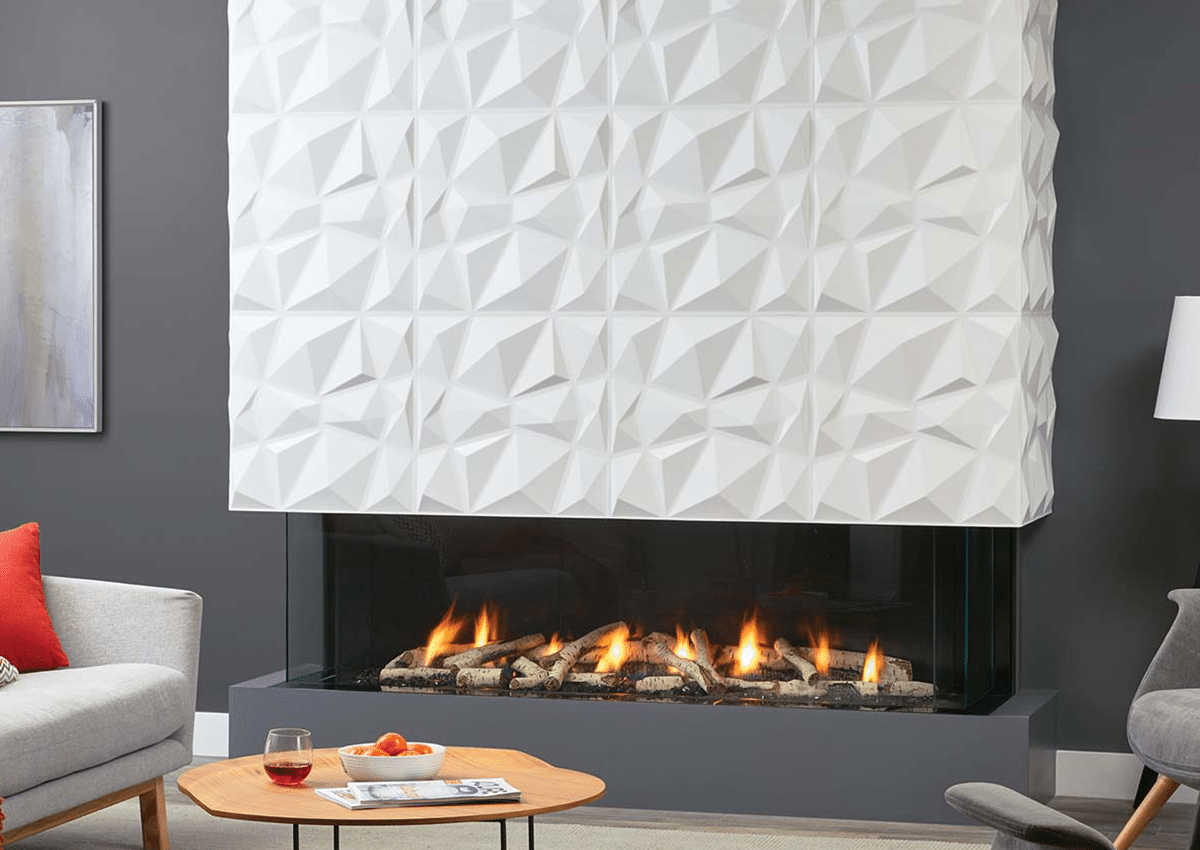
Gas Fireplaces
Gas fireplaces provide more consistent and controllable heat. Typical residential models deliver 20,000 to 40,000 BTU per hour of heat to the room, with some larger or high-output models exceeding 50,000 to 70,000 BTU per hour.
Efficiency depends on the design of the fireplace and venting, but most gas fireplaces are capable of heating medium to large rooms effectively. Gas fireplaces are convenient, require minimal maintenance, and many units remain operational during power outages with battery-assisted ignition systems.
Electric Fireplaces
Electric fireplaces convert nearly all the electricity they use into heat within the room. Standard models typically produce 4,000 to 9,000 BTU per hour, while higher-output units can reach around 10,000 BTU per hour. Electric fireplaces are best for supplemental heating or zone heating in small to medium-sized rooms. They are easy to install, require minimal maintenance, and do not need venting.
Key Takeaways
Fireplaces differ significantly in their ability to provide heat. Traditional wood fireplaces offer a strong visual and sensory experience but deliver limited practical heat. Gas fireplaces provide reliable, moderate to high heat suitable for room or zone heating. Electric fireplaces are efficient and convenient for supplemental heat, but they generally provide lower overall heat output compared with wood or gas models. Understanding BTU ratings and efficiency helps homeowners make informed decisions about which fireplace type best meets their winter heating needs.
Expert Guidance from Team Harding
If you need guidance when choosing a fireplace for your home, Team Harding Comfort can help. Our experienced team can walk you through the different options, explain how each type performs in terms of heat output, and help you select the fireplace that best meets your space, style, and heating needs.
Need help choosing the right fireplace?
Visit our showroom at 200 Nipissing Ct, Kanata.
Follow us on Instagram and Facebook!
Team Harding is Ottawa’s go-to destination for grills, fireplaces, and outdoor heat options. We’re stocked with the brands you know and love.